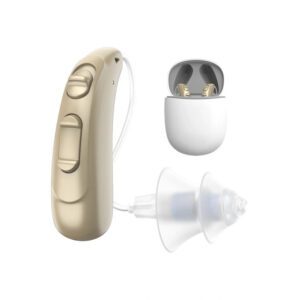
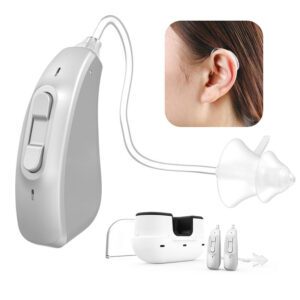
Do you know there are Over-the-Counter (OTC) Hearing Aids? OTC Hearing Aids can be sold in stores and online now.
In October 2022, the FDA finalized its long-awaited OTC hearing aid guidance. The FDA says the goal is to increase competition and ultimately make them more affordable.
Table of Contents:
- What are over-the-counter (OTC) Hearing Aids?
- Pros and Cons of Over-the-Counter (OTC) Hearing Aids
- Six keys between prescription and OTC Hearing Aids
- Who are Over-the-Counter (OTC) Hearing Aids for?
- Who Shouldn’t Use OTC Hearing Aids?
- Where can I buy OTC Hearing Aids?
- Custom wholesale and retail OTC Hearing Aids
What are over-the-counter (OTC) Hearing Aids?
The FDA defines OTC hearing aids as medical devices intended to treat mild to moderate hearing loss in adults 18 years of age and older. They are classified separately from prescription hearing aids, each with its own set of safety and efficacy regulations.
Over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids are a new type of hearing aid that consumers can purchase without visiting a Hearing Health professional. These devices are designed to help adults with mild to moderate hearing loss. Like prescription hearing aids, OTC hearing aids make the sound louder so some adults with hearing impairments are better able to hear, communicate and participate fully in everyday activities.
OTC hearing aids are an alternative to prescription hearing aids and are currently only available from hearing health professionals such as audiologists, otolaryngologists (ear, nose and throat doctors), and hearing aid specialists. A hearing health professional fits your hearing aids, adjusts equipment for your hearing loss, and provides other services. You can buy OTC hearing aids directly at non-prescription hearing aid stores and online. You can install them yourself, and you can control and adjust the device in ways that prescription hearing aid users cannot. Some OTC hearing aids may not look like prescription hearing aids at all.
OTC hearing aids are for adults who experience mild to moderate hearing loss. They are not for use in children or adults with severe hearing loss or significant difficulty hearing. If your hearing loss is more severe, OTC hearing aids may not amplify sound high enough to help you.
Pros and Cons of Over-the-Counter (OTC) Hearing Aids
Over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids can be an excellent solution for many hearing loss people, but they do have drawbacks compared to prescription hearing aids. Let’s take a look at the pros and cons, so you can make an informed decision about which type of hearing aid is right for you.
Pros
Over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids have a range of advantages worth considering:
- People with mild and moderate hearing loss have more choices
OTC hearing aids expand choices for people 18 years of age and older who have perceived mild to moderate hearing impairment. - The price is more affordable
Compared with prescription hearing aids, the price may be much cheaper, and the price of OTC hearing aids is about one-eighth of prescription hearing aids. - Convenient and quick
Hearing aids that can be bought directly in pharmacies, supermarkets or online without hearing tests or fittings, convenient and fast. - It is beneficial to improve the wearing rate of hearing aids
Despite the high prevalence and public health impact of hearing loss, only about one in five people would benefit from hearing aids. One of the main reasons for the low adoption rate is the high price. In addition, it is not easy for hearing friends in some areas to obtain professional hearing tests and fitting adjustments, and it often takes a lot of time and money. - Promote more product research and development and increase industry competition.
Cons
Of course, where there are advantages, there are disadvantages. No hearing aid is without disadvantages, so here are some factors worth considering:
- The user purchases it by himself, and the wearing effect is unknown. If he is not satisfied, it will easily lead to the perception that “hearing aids are useless”.
- Not suitable for those under the age of 18, or with severe and above hearing loss.
- For unilateral hearing loss, sudden deafness, conductive hearing loss, etc., if you buy OTC hearing aids directly, the condition may be delayed.
- Self-fitting, which means they cannot be custom-fitted to fit your ear.
- Typically offers fewer features than prescription hearing aids.
- No on-site hearing care is provided after the purchase.
Six keys between prescription and OTC hearing aids
| Key | Prescription Hearing Aids | OTC Hearing Aids |
|---|---|---|
| Who fits them? | Licensed audiologist or hearing instrument specialist | Self-fit, ordered online or purchased at the store |
| Price | Varies widely, but generally $2k to $7k | Varies widely, as low as $200 but higher-quality models can be up to $2k |
| Diagnosis & testing | Conducted by the provider using advanced testing and diagnostic tools | Approximated by self, depending on the product purchased |
| Design | Full range, including discreet custom-fit options | Limited; one-size-fits-most |
| Degree of hearing loss | Mild, moderate, severe, and profound levels of hearing loss | Self-perceived mild to moderate only |
| Intended user | Any age, any medical status | 18+, best for people without complex ear conditions |
Who are Over-the-Counter (OTC) hearing aids for?
Over-the-counter (OTC) Hearing aid is designed for adults 18 years and older who have mild to moderate hearing loss, even if they haven’t had a hearing test. You may have mild to moderate hearing loss if:
- Speech or other voices seem muffled.
- You can have hearing problems when you are in crowds, in noisy areas, on the phone, or when you can’t see who is speaking.
- You have to ask people to speak more slowly or clearly, speak louder, or repeat what they said.
- When watching TV, listening to the radio, or listening to music, you turn the volume up higher than other people prefer.
Who Shouldn’t Use OTC Hearing Aids?
The over-the-counter hearing aid is not for everyone. According to the FDA, you should not use an OTC hearing aid if:
- you have severe hearing loss
- you are under 18
- You have unilateral (one-side) hearing loss
- you have sudden hearing loss
- You have hearing loss due to a medical condition
- You’re not sure if you have hearing loss (maybe excess earwax!)
- You have frequent dizziness (vertigo) or ringing in the ears (ringing in the ears)
- your ears often hurt
- You have a unique ear anatomy
- You have a history of ear disease/infection
- You have a history of chemotherapy or radiation exposure to the head and neck
- you want more features
Where can I buy OTC hearing aids?
Some manufacturers already offer direct-to-consumer (DTC) hearing aids online, such as our AUDIOTOP® Hearing Aids. DTC means that hearing aids are sold directly to consumers (not through hearing clinics).
Effective October 17, 2022, you can buy Over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids at supermarkets, pharmacies, hearing clinics, hearing centers, amazon, Walmart, online shops, etc.
Custom wholesale and retail OTC hearing aids
Spieth engages in the R&D, production, and sales of Hearing Aids and other acoustic related products, and is committed to improving the hearing of the hearing impaired through technology. We can provide both OEM and ODM hearing aid service, which means size, quantity, design, packing solution, etc will depend on your requests and your logo will be customized on our products. If you are looking for a reliable hearing aid supplier, please contact us.
-
 AUDIOTOP® серии Q Перезаряжаемые слуховые аппараты CIC, магнитно-контактная зарядная коробка с большей емкостью$255.00 – $807.00
AUDIOTOP® серии Q Перезаряжаемые слуховые аппараты CIC, магнитно-контактная зарядная коробка с большей емкостью$255.00 – $807.00 - Product on sale
 AUDIOTOP® Перезаряжаемые слуховые аппараты RIC с блоком питания, 16 каналов$209.00
AUDIOTOP® Перезаряжаемые слуховые аппараты RIC с блоком питания, 16 каналов$209.00 - Product on sale
 AUDIOTOP® Недорогие Перезаряжаемые слуховые аппараты BTE Open Fit, 11 каналов$158.00
AUDIOTOP® Недорогие Перезаряжаемые слуховые аппараты BTE Open Fit, 11 каналов$158.00 -
 AUDIOTOP® Цифровой приемник в канале (RIC) Слуховые аппараты, 4 канала$278.00 – $499.00
AUDIOTOP® Цифровой приемник в канале (RIC) Слуховые аппараты, 4 канала$278.00 – $499.00 -
 AUDIOTOP® Digital BTE слуховые аппараты открытого типа, 4 канала$225.00
AUDIOTOP® Digital BTE слуховые аппараты открытого типа, 4 канала$225.00 -
 AUDIOTOP® Слуховых аппарат Audiotop Полностью в канале (CIC), серии T$165.00 – $524.00
AUDIOTOP® Слуховых аппарат Audiotop Полностью в канале (CIC), серии T$165.00 – $524.00