Enhancing Auditory Experience
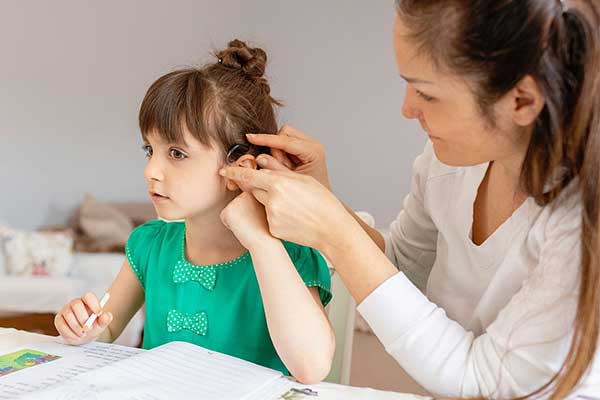
hearing Aids serve as advanced devices catering to individuals with hearing Impairments. These sophisticated tools operate on cutting-edge technology, employing various mechanisms to improve sound perception and communication.
Components and Basic Operation
The fundamental components of a hearing aid include a microphone, amplifier, receiver, and power source. The microphone captures surrounding sounds, converting them into electrical signals. These signals are then amplified by the device’s amplifier, customized to the user’s specific hearing needs. Finally, the receiver transforms the amplified signals back into sound waves, delivering them to the ear canal.
Directional Microphones for Enhanced Clarity
Modern hearing Aids often feature directional microphones, enabling users to focus on specific sounds while minimizing background noise. This functionality enhances speech clarity in noisy environments, facilitating more effective communication.
Digital Signal Processing (DSP) for Real-Time Adaptation
Digital Signal Processing is integral to hearing aid technology. It enables real-time analysis and processing of sound, adapting to different environments and adjusting amplification levels accordingly. This ensures a customized and optimized listening experience in various situations.
Addressing Feedback Challenges
Feedback or whistling sounds are common challenges in hearing aids. To counter this issue, feedback suppression technology is incorporated, identifying and eliminating unwanted feedback. This ensures a clear and comfortable listening experience for the user.
Programmability for Personalized Solutions
Modern hearing aids are programmable, allowing audiologists to customize settings based on the user’s unique hearing profile. This feature ensures a personalized and adaptive solution, accommodating changes in hearing levels over time.
Wireless Connectivity for Enhanced Accessibility
Many hearing aids now come equipped with wireless connectivity features. This allows users to connect their devices to smartphones, televisions, and other audio sources, facilitating the direct streaming of phone calls, music, and other content to their hearing aids. This connectivity enhances overall accessibility.
Conclusion: Empowering a Fuller Engagement
In conclusion, hearing aids significantly contribute to improving the quality of life for individuals with hearing impairments. Through features such as directional microphones, digital signal processing, feedback suppression, programmability, and wireless connectivity, these devices offer a personalized and enhanced auditory experience. This empowerment enables users to more fully engage in the world around them, fostering a greater sense of connection and participation.