Isolation Booth: Ensuring Reliable hearing Diagnostics
The Isolation Booth, often referred to as an audiometry room, is designed specifically for clinical hearing diagnostics, like pure tone threshold tests and suprathreshold function audiometry. To guarantee accurate hearing tests, the booth must maintain a high level of quietness, with indoor noise levels ideally below 26dB.
This is achieved by creating a barrier against external noise through smooth outer wall surfaces for sound reflection, while porous sound-absorbing materials on the inner walls, along with a layered design using rock wool, gypsum, glass wool, and velvet, enhance sound absorption and reduce reverberation within the booth.
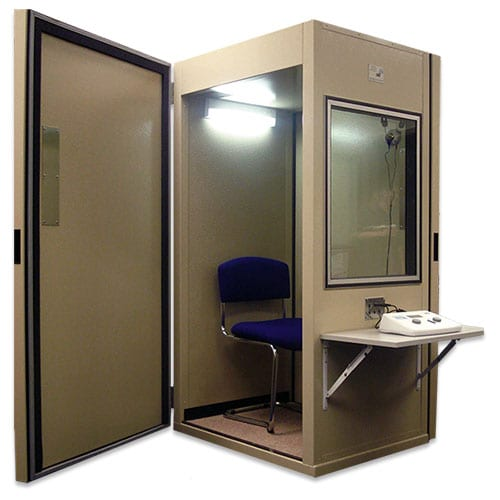

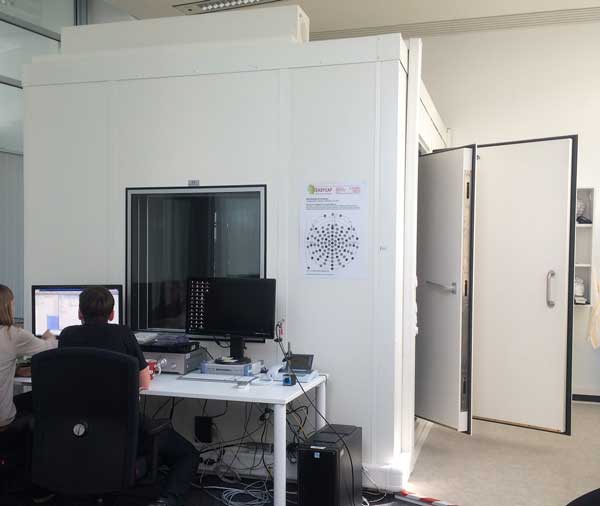
Isolation Shielding Booth: Minimizing Interference in Audiology Testing
In clinical audiology testing that involves recording EEG responses induced by sound, a special environment is essential to prevent interference from environmental noise, AC electric fields, and electromagnetic fields.
This need led to the development of the Isolation Shielding Booth, which combines sound insulation with electromagnetic shielding, ensuring accurate results by eliminating noise and field interference that could impact sensitive test equipment.

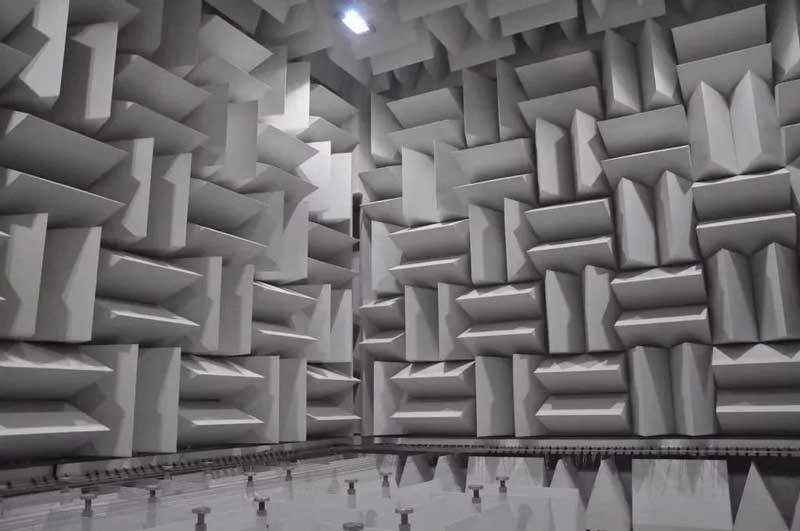
Anechoic Chamber: Achieving Precision in Acoustic Testing
Anechoic chambers serve as specialized acoustic laboratories, integral to sound testing systems where the absence of reflected sound is crucial. This environment, referred to as a “free field” or “semi-free field” space, is characterized by the presence of only direct sound.
Constructed with sound-absorbing wedges or resonant structures, these chambers enable accurate acoustic measurements by maintaining minimal reverberation. Anechoic chambers are classified as either full anechoic, with sound-absorbing surfaces on all six sides, or semi-anechoic, with sound-absorbing surfaces on four or five sides.

Comparing Isolation Booths, Isolation Shielding Booths, and Anechoic Chambers
While a standard Isolation Booth requires only sound insulation, the Isolation Shielding Booth adds electromagnetic shielding to prevent interference, making it suitable for auditory physiology research and auditory evoked potential testing.
In contrast, anechoic chambers demand higher noise control and specialized construction with advanced sound-absorbing materials to eliminate echoes entirely. The complexity of anechoic chambers leads to higher construction costs but is necessary for applications requiring precision in sound testing.