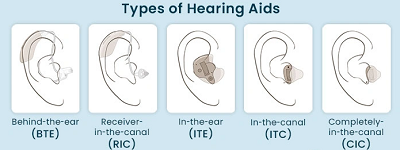
When selecting a hearing aid, it’s important to consider various factors to ensure the device works best for your specific hearing requirements. This process should follow a scientific, personalized approach to achieve optimal results, addressing the individual needs of the patient. This article outlines the key steps in choosing the most suitable hearing aid.
Understanding Your hearing Loss
For patients with sensorineural hearing loss, the type and degree of hearing impairment are critical in determining the appropriate hearing aid. If hearing loss is less than 80 dB HL, hearing Aids are typically the preferred option. However, if hearing loss exceeds 80 dB HL and cochlear implantation is temporarily unsuitable, it is still essential to select an appropriate hearing aid.
Scientific Selection Process
Choosing a hearing aid involves a strict and scientific procedure, ensuring that the device is tailored to the specific needs of the patient. Factors such as age, the nature and degree of hearing loss, and personal preferences must be taken into account to deliver the best hearing experience. Audiologists play a key role in this process by conducting a thorough medical evaluation to identify any contraindications to fitting a hearing aid.
Step 1: Audiological Evaluation
The first step in choosing a hearing aid is an audiological evaluation. The audiologist collects comprehensive information about the patient’s medical history, ear health, and hearing status.
This includes a general otolaryngological examination, hearing tests, and discussions about the patient’s lifestyle and communication needs. Factors such as the patient’s ability to communicate verbally, their social or work environments, and their previous experience with hearing aids (if any) are also considered.
Step 2: Selecting the Right Hearing Aid
The next step is selecting a hearing aid that meets the patient’s needs. This involves considering factors such as price, appearance, and ease of use. The audiologist uses the results of the hearing tests to determine the technical requirements of the hearing aid, such as gain, output, and frequency response.
Using specific formulas and testing tools, the audiologist ensures that the chosen hearing aid will provide the appropriate amplification for the patient’s hearing profile.
Step 3: Adapting to the Hearing Aid
For first-time hearing aid users, adaptation is crucial. Initially, it is recommended to wear the device in a quiet environment to get accustomed to the new sounds. It is normal to experience some fatigue, so the patient should gradually increase the wearing time.
Over time, the patient should be able to wear the hearing aid in various environments to achieve the desired listening effect.
Step 4: Evaluating the Effectiveness
After the initial fitting, the patient’s progress is monitored through follow-up evaluations. This may include conversations with the patient, functional gain testing, and real ear analysis to assess improvements in hearing and speech comprehension. The audiologist can adjust the hearing aid settings based on the patient’s feedback and test results.
Step 5: Regular Follow-ups and Adjustments
Choosing the right hearing aid is not a one-time process. Continuous evaluation and adjustment are necessary to ensure that the hearing aid remains effective over time.
Regular hearing tests and performance checks should be conducted to confirm that the hearing aid continues to meet the patient’s needs. After wearing the device for a while, patients should return to the fitting department for any necessary adjustments, ensuring that the hearing aid remains in optimal working condition.
Conclusion
Selecting the most suitable hearing aid involves a thorough and personalized process, with continuous evaluations to ensure the device continues to meet the patient’s needs. By following these steps, individuals with hearing loss can achieve significant improvements in their hearing ability and overall quality of life.