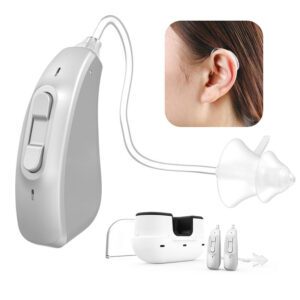
What is a balanced armature?
A Balanced Armature (BA) is a type of transducer or driver used in audio devices to convert electrical signals into sound. It’s a specific technology employed in hearing Aids, earphones, headphones, and other audio equipment. The term “balanced” refers to the way the armature is balanced between the poles of a magnet.
Spieth’s Main Balanced Armature
| Series | Picture | Dimension(mm) | Features |
| SBAB-25 |  | 5.0×2.73×1.93mm | Small size, Max. output achieve 124dB. Can be used in CIC hearing Aids. |
| SBAB-26 |  | 52.822.03mm | Small size, tweeter. |
| SBAB-30 |  | 5.06×2.78×2.59mm | Small size, Max. output achieve 124dB. Can be used in CIC hearing Aids. |
| SBAB-40 |  | 5.15×2.96×2.58mm | Small size, Max. output achieve 124dB. Can be used in CIC or ITC Hearing Aids. Can be used in earphones, and improved low-frequency performance. |
| SBAB-50 | 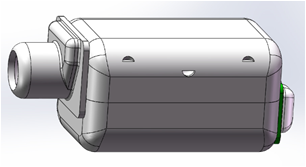 | 5.11×3.46×2.95mm | Middle size, Max. output achieve 123dB. Can be used in ITC or ITE Hearing Aids. |
| SBAB-80 | 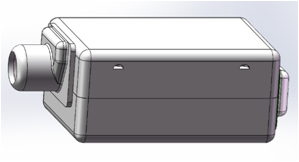 | 6.37×4.35×2.96mm | Middle size, Max. output achieve 126dB. Can be used in ITE or BTE hearing Aids. |
| SBAB-280 | 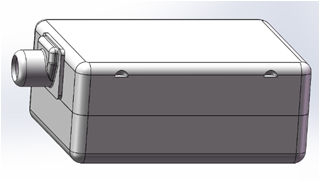 | 9.47×7.19×4.06mm | Max. output achieve 140dB. Can be used in BTE Hearing Aids. |
| SBADB-45 | 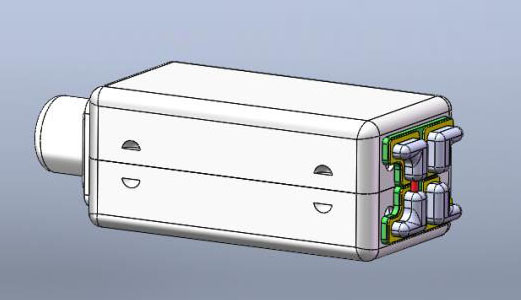 | 6.03.122.59mm | Dual receiver Small size, Max. output achieve 127dB. Can be used in CIC, RIC, and mini BTE Hearing Aids. |
| SBADB-50 |  | 5.0×2.73×3.92mm | Dual receiver Small size, Max. output achieve 124dB. Can be used in ITE Hearing Aids。 |
| SBADB-180 |  | 7.86×4.16×5.56mm | Dual receiver Small size, Max. output achieve 138dB. Can be used in BTE hearing Aids. |
How does a balanced armature work?
The working principle of Balanced Armature (BA) drivers involves the interaction of magnetic fields and a suspended armature within a coil. Here’s a simplified explanation of how it works:
Coil and Armature:
- The BA driver consists of a small, lightweight armature (a coil of wire) that is suspended between the poles of a permanent magnet.
- The armature is typically balanced between two magnets, creating a balanced system.
Incoming Electrical Signal:
- When an electrical audio signal is sent to the coil, it creates an electromagnetic field around the coil.
Interaction with Magnetic Field:
- The magnetic field produced by the permanent magnets interacts with the electromagnetic field around the coil.
- This interaction causes the armature to move back and forth within the magnetic field.
Diaphragm Movement:
- The movement of the armature is transmitted to a diaphragm (a thin, lightweight membrane) attached to it.
- As the armature moves, it causes the diaphragm to vibrate.
Sound Production:
- The vibrations of the diaphragm result in the creation of sound waves that correspond to the electrical audio signal.
Frequency Response:
- The design of the BA driver, including the properties of the armature and diaphragm, influences the frequency response and the driver’s ability to reproduce different frequencies accurately.
Multiple Drivers and Crossovers:
- In some applications, multiple BA drivers with different frequency responses may be used together to cover a wider range of frequencies.
- Crossover networks are employed to divide the audio signal among the different drivers, ensuring each handles the appropriate frequency range.
Key features of Balanced Armature technology:
Size and Design:
- BA drivers are relatively small and lightweight compared to other driver technologies like dynamic drivers.
- The compact size allows for the creation of in-ear monitors (IEMs) and hearing aids with a more discreet and comfortable form factor.
Efficiency:
- Balanced Armature drivers are efficient in converting electrical signals into sound waves.
- They typically require less power to produce a given sound level, making them suitable for applications with limited power resources, such as hearing aids.
Precision and Accuracy:
- BA drivers are known for their precision and accuracy in reproducing sound across the frequency spectrum.
- They are capable of producing detailed and clear audio, especially in the mid to high-frequency ranges.
Crossover Networks:
- BA drivers are often used in conjunction with multiple drivers and crossover networks in high-end audio equipment.
- This allows for better control over different frequency ranges, enhancing the overall audio quality.